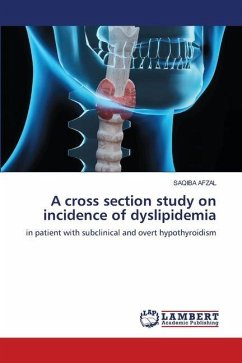
The thyroid (Greek thyreos, shield, plus edios, form) consists of two lobes that are connected by an isthmus(1). The English anatomist Thomas Wharton was the first to coin the Latin expression for the thyroid gland(2). It is a butterfly-shaped organ and is composed of two lobes or wings, Lobus dexter (Right-lobe)and Lobus sinister (Left-lobes),connected via the Isthmus and is one of the Largest endocrine glands found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage. There is occasionally (28-55% of population,mean 44.3%), a third lobe present called the pyramidal lobe of the thyroid gland (3,) which is conical in shape and extends from the upper part of the isthmus up across the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone.The thyroid gland controls how quickly, the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls how sensitive the body is to other hormones.The thyroid gland produces two related hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyroxine (T3). Acting through nuclear receptors, these hormones play a critical role in cell differentiation during development and help maintain thermogenic and metabolic homeostasis in the adults(1) .
Bitte wählen Sie Ihr Anliegen aus.
Rechnungen
Retourenschein anfordern
Bestellstatus
Storno