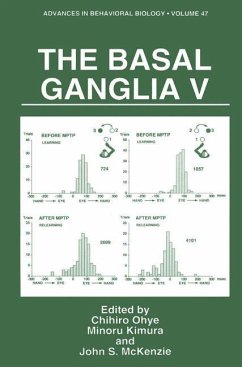
Basal ganglia disease
Versandkostenfrei!
Versandfertig in 6-10 Tagen
42,99 €
inkl. MwSt.

PAYBACK Punkte
21 °P sammeln!
Please note that the content of this book primarily consists of articles available from Wikipedia or other free sources online. Basal ganglia disease refers to a group of physical dysfunctions that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly suppress unwanted movements or to properly prime upper motor neuron circuits to initiate motor function. Research indicates that increased output of the basal ganglia inhibits thalamocortical projection neurons. Proper activation or deactivation of these neurons is an integral component for proper movement. If so...
Please note that the content of this book primarily consists of articles available from Wikipedia or other free sources online. Basal ganglia disease refers to a group of physical dysfunctions that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly suppress unwanted movements or to properly prime upper motor neuron circuits to initiate motor function. Research indicates that increased output of the basal ganglia inhibits thalamocortical projection neurons. Proper activation or deactivation of these neurons is an integral component for proper movement. If something causes too much basal ganglia output, then the thalamocortical projection neurons become too inhibited and one cannot initiate voluntary movement. These disorders are known as a hypokinetic disorders. However, a disorder leading to abnormally low output of the basal ganglia leads to relatively no inhibition of the thalamocortical projection neurons. This situation leads to an inability to suppress unwanted movements. These disorders are known as hyperkinetic disorders. Currently, reasons for abnormal increases or decreases of basal ganglia output are poorly understood.