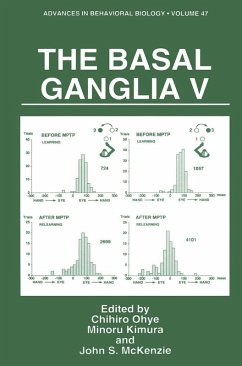
Basal Ganglia
Versandkostenfrei!
Versandfertig in 6-10 Tagen
39,99 €
inkl. MwSt.

PAYBACK Punkte
20 °P sammeln!
The basal ganglia (or basal nuclei) are a group of nuclei in the brains of vertebrates, situated at the base of the forebrain and strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including motor control and learning. Currently popular theories implicate the basal ganglia primarily in action selection, that is, the decision of which of several possible behaviors to execute at a given time. Experimental studies show that the basal ganglia exert an inhibitory influence on a number of motor systems, and that a rele...
The basal ganglia (or basal nuclei) are a group of nuclei in the brains of vertebrates, situated at the base of the forebrain and strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including motor control and learning. Currently popular theories implicate the basal ganglia primarily in action selection, that is, the decision of which of several possible behaviors to execute at a given time. Experimental studies show that the basal ganglia exert an inhibitory influence on a number of motor systems, and that a release of this inhibition permits a motor system to become active. The "behavior switching" that takes place within the basal ganglia is influenced by signals from many parts of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, which is widely believed to play a key role in executive functions. The main components of the basal ganglia are the striatum, pallidum, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus. The largest component, the striatum, receives input from many brain areas but sends output only to other components of the basal ganglia.