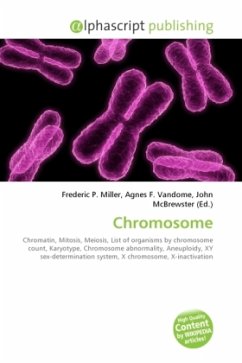
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein that is found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. The word chromosome comes from the Greek (chroma, color) and (soma, body) due to their property of being very strongly stained by particular dyes. Diagram of a duplicated and condensed metaphase eukaryotic chromosome. (1) Chromatid one of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase. (2) Centromere the point where the two chromatids touch, and where the microtubules attach. (3) Short arm. (4) Long arm. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. The DNA molecule may be circular or linear, and can be composed of 10,000 to 1,000,000,000 nucleotides in a long chain. Typically eukaryotic cells (cells with nuclei) have large linear chromosomes and prokaryotic cells (cells without defined nuclei) have smaller circular chromosomes, although there are many exceptions to this rule.
Bitte wählen Sie Ihr Anliegen aus.
Rechnungen
Retourenschein anfordern
Bestellstatus
Storno