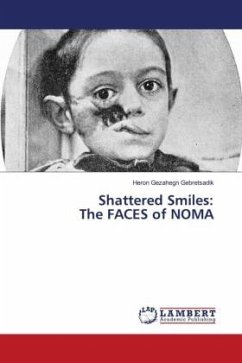
Eradication of poverty through foreign charity to fight tb in Kisii
TB is the leading cause of deaths among the poor households in Kisii Kenya
Versandkostenfrei!
Versandfertig in 6-10 Tagen
30,99 €
inkl. MwSt.

PAYBACK Punkte
15 °P sammeln!
Tuberculosis remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality in Kenya. It affects all age groups, but has its greatest toll in the most productive age group of 15 to 44 years. The major factor responsible for the large TB disease burden in Kenya is the concurrent HIV epidemic.There are now plans in place to continue to improve the quality of programme data through the use of electronic reporting and recording systems, to strengthen community involvement in TB control, to engage all health service providers in the control of TB, to strengthen TB control in congregate settings, to re-examine th...
Tuberculosis remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality in Kenya. It affects all age groups, but has its greatest toll in the most productive age group of 15 to 44 years. The major factor responsible for the large TB disease burden in Kenya is the concurrent HIV epidemic.There are now plans in place to continue to improve the quality of programme data through the use of electronic reporting and recording systems, to strengthen community involvement in TB control, to engage all health service providers in the control of TB, to strengthen TB control in congregate settings, to re-examine the control of TB in nomadic areas, and finally to strengthen the control and treatment of drug-resistant TB.