Herpes Zoster
Versandkostenfrei!
Versandfertig in 6-10 Tagen
23,99 €
inkl. MwSt.

PAYBACK Punkte
12 °P sammeln!
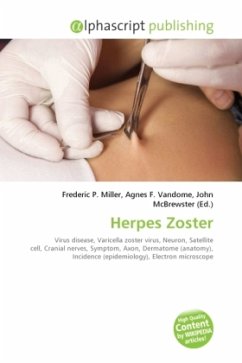
Herpes zoster (or simply zoster), commonly known as shingles and also known as zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a limited area on one side of the body, often in a stripe. The initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV) causes the acute (short-lived) illness chickenpox, and generally occurs in children and young people. Once an episode of chickenpox has resolved, the virus is not eliminated from the body but can go on to cause shingles an illness with very different symptoms often many years after the initial infection. Varicella zoster viru...
Herpes zoster (or simply zoster), commonly known as shingles and also known as zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a limited area on one side of the body, often in a stripe. The initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV) causes the acute (short-lived) illness chickenpox, and generally occurs in children and young people. Once an episode of chickenpox has resolved, the virus is not eliminated from the body but can go on to cause shingles an illness with very different symptoms often many years after the initial infection. Varicella zoster virus can become latent in the nerve cell bodies and less frequently in non-neuronal satellite cells of dorsal root, cranial nerve or autonomic ganglion, without causing any symptoms. In an immunocompromised individual, perhaps years or decades after a chickenpox infection, the virus may break out of nerve cell bodies and travel down nerve axons to cause viral infection of the skin in the regionof the nerve. The virus may spread from one or more ganglia along nerves of an affected segment and infect the corresponding dermatome (an area of skin supplied by one spinal nerve) causing a painful rash.












