Nano Porous Aluminum Oxide Film
Fabrication and Characterization
Versandkostenfrei!
Versandfertig in 6-10 Tagen
36,99 €
inkl. MwSt.

PAYBACK Punkte
18 °P sammeln!
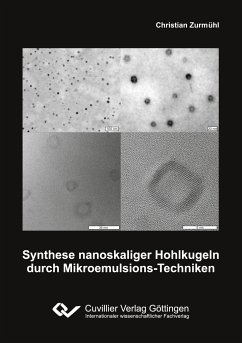
Porous anodic aluminum oxide film is resulted from anodizing of aluminum in acidic solution. This oxide film is so vital for many applications fabrication. The effect of various anodization parameters like voltage, temperature and electrolyte concentration on the process and the resulted film, were studied. The resulted porous anodic alumina film was characterized by SEM, EDX, XRD, image analysis. Electrical capacitance and impedance measurements were taken for each condition. Theoretical calculations concerning weight change and anodization efficiency were conducted. SEM image analysis showed...
Porous anodic aluminum oxide film is resulted from anodizing of aluminum in acidic solution. This oxide film is so vital for many applications fabrication. The effect of various anodization parameters like voltage, temperature and electrolyte concentration on the process and the resulted film, were studied. The resulted porous anodic alumina film was characterized by SEM, EDX, XRD, image analysis. Electrical capacitance and impedance measurements were taken for each condition. Theoretical calculations concerning weight change and anodization efficiency were conducted. SEM image analysis showed that increasing anodizing voltage, temperature, or electrolyte concentration increases pore diameter. X-rays diffraction showed non-crystallinity of alumina film. Capacitance measurements showed a high ability of porous alumina layer to store electric charges and this ability decreases as the anodization voltage, temperature, and electrolyte concentration increase.