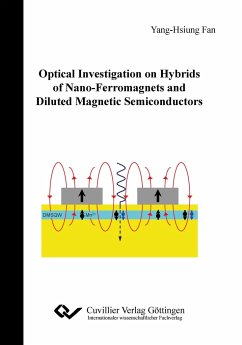
The main aspect of this work is to study a hybrid structure made of metallic ferromagnet (FM) on top of a semiconductor to prove possibilities of spin control via the stray field of a FM. To achieve an effective sensitivity, a diluted magnetic II-VI semiconductor quantum well (DMSQW) is used, where a film ZnCdMnSe well is used to prove the stray field at a fixed distance from the FM. The s,p-d exchange interaction between magnetic Mn ions and band electrons leads to the giant Zeeman effect with g-factors in the order of 500 at low temperature (T ¿ 1.5 K). In typical DMSQW with zinc blende symmetry and compressive strain, the exchange interaction of the exciton ground-state is dominated by the p-d coupling of the heavy-hole which has a negligible in-plane magnetic moment and interacts thus mainly with a field component along the quantum well growth direction z.
Hinweis: Dieser Artikel kann nur an eine deutsche Lieferadresse ausgeliefert werden.
Hinweis: Dieser Artikel kann nur an eine deutsche Lieferadresse ausgeliefert werden.