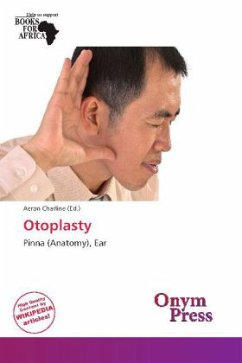
Otoplasty denotes the surgical and non-surgical procedures for correcting the deformities and defects of the external ear (pinna); and for reconstructing a missing ear, consequent to congenital conditions (e.g. microtia, anotia, etc.) and trauma (blunt, penetrating, blast). The otoplastic surgeon creates an external ear of natural proportions, contour, and appearance, by reshaping, moving, and augmenting the cartilaginous framework of the pinna. Moreover, because the occurrence of congenital ear deformities occasionally overlaps with other medical conditions (e.g. Treacher Collins Syndrome, Hemifacial microsomia, etc.), otoplasty procedures also are performed by an oro-maxilofacial surgeon (mouth, jaw, face specialist), an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, throat specialist), and the usual plastic surgeon.