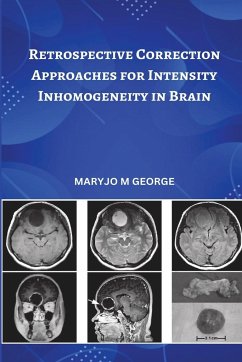
MRI has been growing as a widely preferred modality for structural brain imaging. Intensity inhomogeneity is one of the prime obstacles in the automatic MR image processing algorithms. Retrospective correction strategies for the correction of this artifact have been found to be more useful in clinical practices in comparison with prospective methods. The retrospective correction strategies are applied directly on the image and therefore can correct for intensity inhomogeneity arising from all the possible sources. The retrospective correction strategies can be broadly classified into filtering, surface fitting, histogram based and segmentation based methods. This thesis contributes improved novel retrospective correction focusing on the adult brain MR images. The methodologies are proposed with specific objectives of reduced predefined parameters that critically affect the correction accuracy, enhancement of conventional filtering methods and fully-automatic segmentation based method. Two novel methodologies have been proposed with minimal user-defined parameters. The first method has been implemented by formulating the inhomogeneity problem considering sparsity constraints in suitable transform domains. While in the second method, a compensation function and a modified diffusion strategy have been developed for intensity inhomogeneity correction. The performance of conventional filtering methods have been improved significantly by considering multiscale frameworks with the focus on reducing edge artifacts. And finally, a segmentation based method has been introduced which is fully-automatic that requires no manual interaction even for parameter initialization.