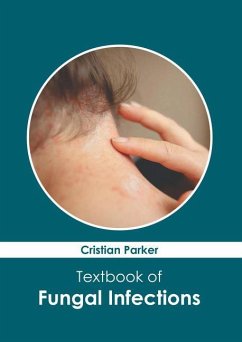
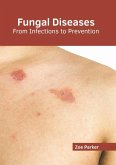
Fungal infections are diseases that are caused by fungus. They can affect the skin, nails, and lungs. Various types of fungal infections have been divided into three categories, namely superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic fungal infections. Subcutaneous fungal infections usually affect tissues beneath the skin, whereas systemic fungal infections can affect organs such as the lungs, eyes, liver, and brain. Some of the major fungal infections include athlete's foot, jock itch, pityriasis versicolor, ringworm, and thrush. The common symptoms of fungal infections vary widely and can include blisters, irritation, itching, redness, scaly skin, swelling, and difficulty in breathing. Immunocompromised people are at an increased risk of fungal infections. The diagnosis of fungal infections can be done using a combination of physical examination and laboratory tests, such as skin or blood cultures. After the type of fungal infection has been diagnosed, the medical practitioners usually prescribe a treatment involving antifungal medications, which may be administered orally or topically. The most common anti-fungal medications include azoles, polyenes, echinocandins, and allylamines. The patients should complete the full course of medicine prescribed to them to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of the fungus. The topics covered in this extensive book deal with the core subject of fungal infections. It will provide comprehensive knowledge to the readers.
Hinweis: Dieser Artikel kann nur an eine deutsche Lieferadresse ausgeliefert werden.
Hinweis: Dieser Artikel kann nur an eine deutsche Lieferadresse ausgeliefert werden.