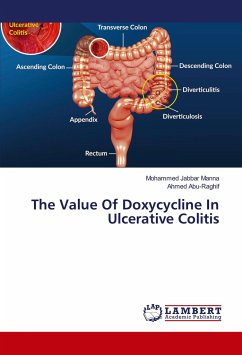
Ulcerative colitis (UC) comprises those conditions characterized by a tendency for chronic relapsing remitting inflammatory disease of the large intestine . The uncertainty of the etiologic factors of ulcerative colitis and the failure of current treatment strategies to control many cases of this disease make a strong stimulus to find out a new relatively safe and effective modality of treatment .Studies pointed to overproduction of free radicals and decreased antioxidant capacity in the pathogenesis of UC both in animal models of induced colitis and human beings. The aim of current study is to investigate the effect of Doxycycline as potential therapy for ulcerative colitis through its effect on inflammatory biomarkers, oxidative stress parameters and histological outcome.
Bitte wählen Sie Ihr Anliegen aus.
Rechnungen
Retourenschein anfordern
Bestellstatus
Storno