New Area-Based Anti-Aliasing for CGI (eBook, ePUB)
Versandkostenfrei!
Sofort per Download lieferbar
33,95 €
inkl. MwSt.
Weitere Ausgaben:

PAYBACK Punkte
17 °P sammeln!
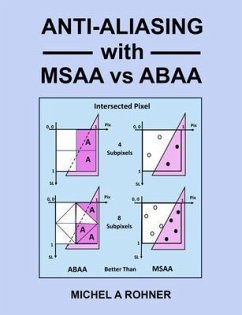
Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) consists of computer applications for creating images in art, printed media, video games, simulators and computer animation. These images consist of 2 dimensional arrays of pixels (picture elements). When images are computed using a single sample per pixels, they show aliasing artifacts such as stairsteps on feature edges (jaggies). In dynamic scenes, aliasing artifacts are amplified, resulting in edge crawling, line breaking and small features popping in-and out. Aliasing artifacts can be minimized, by applying Anti-Aliasing (AA) techniques, such as Super-Samp...
Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) consists of computer applications for creating images in art, printed media, video games, simulators and computer animation. These images consist of 2 dimensional arrays of pixels (picture elements). When images are computed using a single sample per pixels, they show aliasing artifacts such as stairsteps on feature edges (jaggies). In dynamic scenes, aliasing artifacts are amplified, resulting in edge crawling, line breaking and small features popping in-and out. Aliasing artifacts can be minimized, by applying Anti-Aliasing (AA) techniques, such as Super-Sampling (SSAA). With SSAA, static images are computed at higher resolution, then downscaled with filtering. For real-time (RT) CGI applications like computer games and flight simulators, a similar approach consists of Multi-Sample AA (MSAA), With MSAA, several images are computed for a few sample points, followed by images averaging. The MSAA method can be computation intensive and costly. This book has two versions and this is the expanded or more detailed version.
Dieser Download kann aus rechtlichen Gründen nur mit Rechnungsadresse in A, D ausgeliefert werden.